Lean Six Sigma Tools
Lean Six Sigma is the combination of both Lean and Six Sigma methodology which emphasises on two essential components of business processes. It is a process to streamline, improve and optimize every aspect of an organization by eliminating waste and reducing variations.
- The 5S Systems
The 5S System is a workplace organization method that incorporates a list of five words which start with the letter ‘S’. It refers to the five Japanese terms that describe the 5S system of visual management which are Seiri, Seiton, Seiso, Seiketsu and Shitsuke (Michalska & Szewieczek, 2017). These words are translated in English as Sort, Set in Order, Shine, Standardize and Sustain. The aim of this tool is to increase efficiency and productivity.

Image Source: transformanceadvisors.com
5S Systems

- The 5 Whys

Image Source: humanperformancetools.com
Lean Six Sigma resolves a problem by defining and analysing the root cause. 5 Whys is one of the Lean Six Sigma Tools that is deployed as part of the Analyze phase in DMAIC. The implementation of 5 Whys is by repeating the question “Why” which attempts to discover the root cause behind a problem.
5 Whys originated from Japan where Sakichi Toyoda, the founder of Toyota Motor Corporation, invented “5 Whys” technique in order to improve the process of manufacturing. Bathla (2018) explained that whenever there was a lapse or system failure, he would question the employees the reason for it five times in order to get to the root of the problem.
Toyota repeated “Why?” five times to investigate the root cause of a problem in a case that involved a welding robot that stopped in the middle of its operation.
- “Why did the robot stop?”
The circuit has overloaded, causing a fuse to blow.
- “Why is the circuit overloaded?
“There was insufficient lubrication on the bearings, so they locked up.
- “Why is there insufficient lubrication on the bearings?
“The oil pump on the robot is not circulating sufficient oil.
- “Why is the pump not circulating sufficient oil?”
The pump intake is clogged with metal shavings.
- “Why is the intake clogged with metal shavings?”
Because there is no filter on the pump
- Value Stream Mapping
Mukherjee (n.d.) defines Value Stream Mapping as a lean manufacturing technique to analyze, design and manage the flow of information and materials needed to deliver products to customers. It is developed to improve and optimize flow throughout organization as well as making processes compact and precise by eliminating waste.
Value Stream Mapping is an excellent tool to improve delivery chain that requires complex processes. It can be utilized as a tool to understand the entire process by creating a comprehensive view or focus on a segment of the process to address a specific issue.
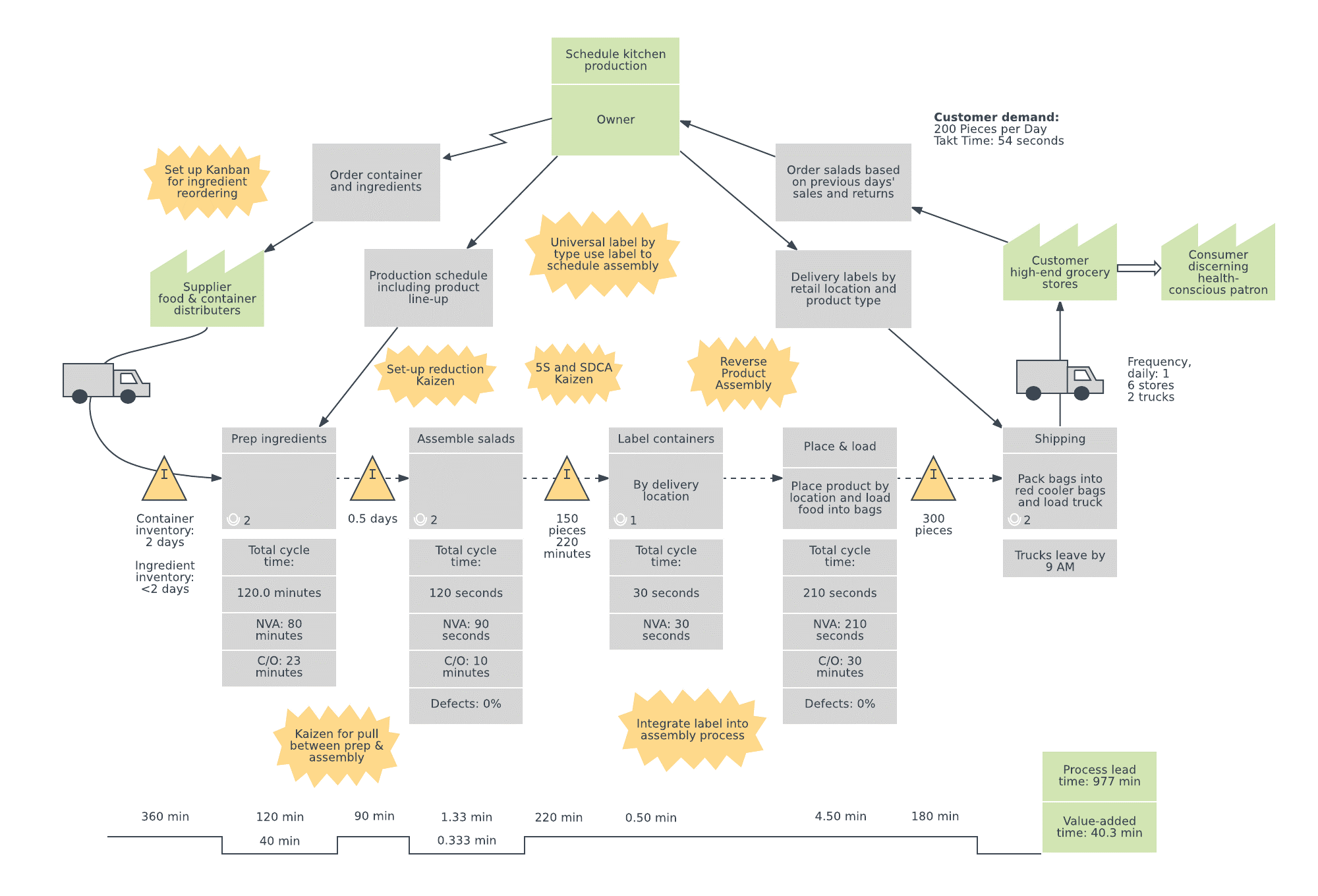
Source: lucidchart.com
Value Stream Mapping is one of the Lean Six Sigma Tools that uses symbols to represent the flow of information and inventory within a system. Incorporated with symbols, it enables visualization of the current state of the process in the organization and help to identify where waste is occurring. This process overview helps an organization to analyze the process workflow, identifying wastes and inefficiencies.

Source: edrawsoft.com
- Regression Analysis
Uyanic and Güler (2013) define regression analysis as a statistical tool to estimate the relationship between variables which are related to result and reason. It includes analyzation on variables that are categorized as dependent variable and independent variables. Dependent variable is the main factor to be analysed while independent variables are the factors that are expected to influence the dependent variable.
There are several types of regression analysis which are used by analyst to study the relationship between variables (Ray, 2015). Linear regression is the most widely known modelling technique of regression analysis which is represented by an equation:
Y= a + b*X + e
| Y | Dependent Variable |
| X | Independent Variable |
| a | Intercept |
| b | Slope of the Line |
| e | Error Term |

Image Source: ablebits.com
Foyer (2018) stated that regression analysis should be used to investigate whether the factor of the hypothesis impacts a portion of a business as it leads to informed business decisions, efficient resources allocation and improved business’ bottom line.
- Poka Yoke
Poka Yoke is derived from the Japanese words, Poka (unintentional mistake that one can make) and Yoke (to prove and prevent) which was developed by Shigeo Shingo in the 1960s (Biswas & Chakraborty, 2016). It is a part of Lean manufacturing tool which is implemented in organizations to achieve operational efficiency. The main purpose of Poka Yoke is to eliminate defects such as inadequate information, unawareness and wrong assumptions that are caused by human errors in manufacturing processes and management.
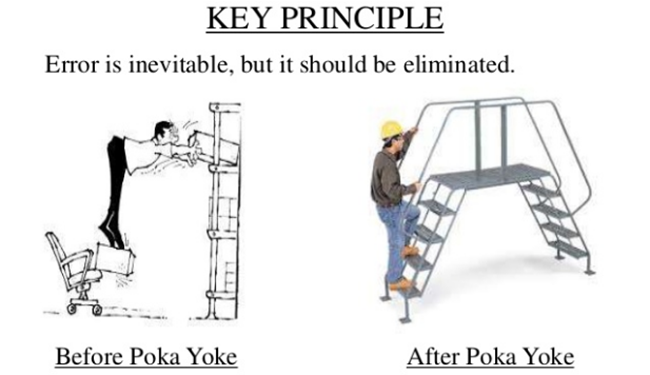
Image Source: latestquality.com
Lin (2018) listed some examples of the implementation of Poka Yoke in everyday life. One of the implementations is the “error-proofing” features of cars. Safety features of cars help to prevent injuries which can be caused by human errors. Sensors, for example, are equipped in cars which help to alarm drivers whenever they are too close to another car or object.
- Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA)
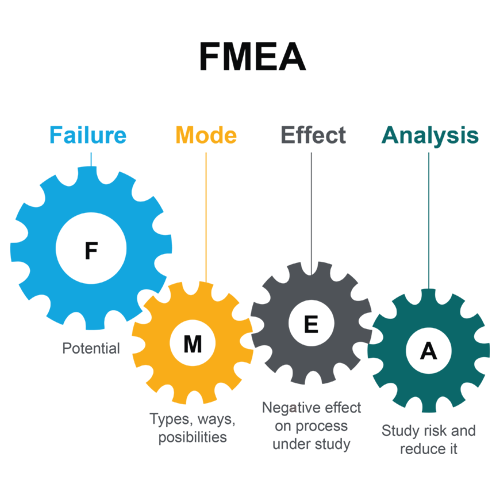
Image Source: sigmasavvy.com
Failure Mode and Effect Analysis (FMEA) is one of the Lean Six Sigma Tools that was developed in 1940s by the U.S military where it is a step-by-step approach to identify possible failures in design, manufacturing or assembly processes (ASQ, n.d.). It was also developed to prevent potential failures of products and processes and their effects.
Failures lead to waste, defects or harmful outcomes to the customers. Hence, it is crucial for failures to be identified early in order to prevent customers and financial losses. According to Institute of Healthcare Improvement (n.d.), teams use FMEA to identify possible failures in a process and improve them rather than correcting the consequences that they bring. FMEA is implemented in healthcare where its focus on prevention may reduce risk or harm to the patients and staff.
Proper implementation of FMEA provides many benefits that can help to improve operational efficiency. It offers a method to select a design that has a high probability of having successful operation and safety, aside from allowing potential failures mechanisms to be assessed. Besides, it also serves as an effective method to evaluate the effects of proposed changes on procedures.
- Kaizen
Kaizen is derived from two Japanese words which are “Kai” (Change) and “Zen” (for the
Better) and thus is defined is “changing for the better. Kaizen is an incremental improvement that emphasizes on permanent efforts of all the people in an organization to attain improvements for outstanding results while understanding management as a way of maintaining and improving working standards (as cited in Alvarado-Ramirez et al, 2018).
One of the main benefits with the implementation of Kaizen is the culture of teamwork within an organization. It encourages employees’ participation and thus, getting them more involved and engaged with the company (Do, 2017). Working environment which incorporates engaged employees results in increased productivity, enhanced employee satisfaction and the list goes on.
Kaizen Improvement Cycle has six phases (Do, 2017):

Image Source: theleanway.net
Kaizen Improvement Cycle begins by identifying the problem or opportunity for improvement. During the analyze phase, the underlying cause of the problem is investigated before developing an optimal solution to address it. The solution is implemented and adjusted according to the needs of an organization. Last but not least, the solution is standardized throughout the organization and efforts to maintain it are required for continuous improvement.
Various Lean Six Sigma tools offer improvements which can be implemented to increase an organization’s operational efficiency. Even though each tool may provide numerous benefits to the organization, it is crucial to select the appropriate tool to cater the organization according to its needs and goals.
References
Alvarado-Ramírez, K. M., Pumisacho-Álvaro, V. H., Miguel-Davila, J. Á., & Suárez Barraza,
- F. (2018). Kaizen, a continuous improvement practice in organizations: a
comparative study in companies from Mexico and Ecuador. The TQM Journal, 30(4),
255-268.
Bathla, S. (2018, August 17). Use This “5-Whys Principle” To Find Real Solution to Any
Problem Quicker. Retrieved from https://medium.com/multiplier-magazine/how-5-whys-principle-can-help-you-find-real-solution-to-any-problem-1e0c05e4d4dd
Biswas, M. S., & Chakraborty, A. Using Poka-Yoke for the Development of SMEs.
Do, D. (2017, August 5). What is Continuous Improvement (Kaizen)? Retrieved from
https://theleanway.net/what-is-continuous-improvement
Foley, B. (2018, February 14). What is Regression Analysis and Why Should I Use It? |
SurveyGizmo Blog. Retrieved from https://www.surveygizmo.com/resources/blog/regression-analysis/
Lin, A. (2018, December 28). Lean in Real Life: 10 Examples of Poka Yoke in Everyday
Life. Retrieved from https://tulip.co/blog/lean-manufacturing/poka-yoke-examples-everyday-life/
Michalska, J., & Szewieczek, D. (2007). The 5S methodology as a tool for improving the
organization. Journal of Achievements in Materials and Manufacturing Engineering, 24(2), 211-214.
Mukherjee, J. (n.d.). Value Stream Mapping. Retrieved from
https://www.atlassian.com/continuous-delivery/principles/value-stream-mapping
Ray, S. (2015, August 14). 7 Types of Regression Techniques you should know. Retrieved
from https://www.analyticsvidhya.com/blog/2015/08/comprehensive-guide-regression/
Uyanık, G. K., & Güler, N. (2013). A study on multiple linear regression analysis. Procedia-
Social and Behavioral Sciences, 106, 234-240.


